Comparing the efficacy of hydroxyapatite nucleation regulated by amino acids, poly-amino acids and an amelogenin-derived peptide†
Abstract
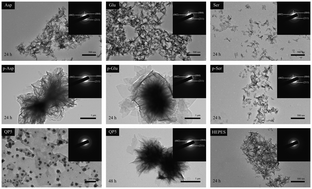
Enamel biomineralization is modulated by biological macromolecules composed of amino acids. Although previous studies have shown that single amino acids, poly-amino acids and peptides regulate hydroxyapatite (HAP) nucleation, their experimental conditions were all different and nobody has compared their efficacy in parallel experiments under the same conditions. In this report, the efficacy of HAP nucleation regulated by single amino acids (aspartic acid, glutamic acid and serine), poly-amino acids (poly-aspartic acid, poly-glutamic acid and poly-serine) and an amelogenin-derived peptide named QP5 was compared systematically using scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and zeta potential. These bioactive components were found to primarily inhibit nucleation in solution and this inhibition showed a tendency to increase as the molecular size increased. Moreover, poly-aspartic acid, poly-glutamic acid and QP5 induced regular flower-like clusters with larger sizes. In situ remineralization experiments showed that QP5 could induce oriented crystal growth along the c-axis. The multi-pathways to crystallization and anion coordination polyhedron growth unit theory explain the regulatory mechanism of biomineralization by the bioactive macromolecules. This is the first systematic comparison of the efficacy of HAP nucleation regulated by single amino acids, poly-amino acids and QP5 in one parallel experiment. The results underpin future research on peptide design and provide a deeper understanding of the mechanism of QP5 in regulating mineralization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...