In situ formation of surface and bulk oxides in small palladium nanoparticles†
Abstract
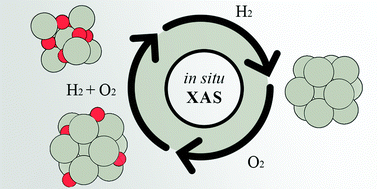
Evolution of surface and bulk palladium oxides in supported palladium nanoparticles was followed in situ using X-ray absorption spectroscopy. The surface oxide was found to be easily reducible in hydrogen at room temperature, while removal of bulk oxide required heating in hydrogen above 100 °C. We also found that the co-presence of hydrogen and oxygen favours a stronger oxidation of palladium particles compared to pure oxygen.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...