A large molecular cluster with high proton release capacity†
Abstract
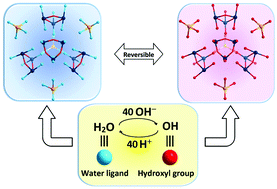
We present a single molecular polyoxometalate cluster (K41[(P2W12Nb6O62)6{Mn3(OH)3(H2O)6}4{Mn3Na(H2O)16}]·26H2O) with controllable release of a large number of protons (∼40 per molecule) in its aqueous solution upon addition of a base. The deprotonation/protonation process is reversible with the clusters remaining intact. This molecule can also absorb up to 11 protons per cluster when an acid, HCl, was added to its original aqueous solution. To the best of our knowledge, such large proton absorption/release capacity along with excellent stability is unprecedented.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
