Accelerating gas–liquid chemical reactions in flow
Abstract
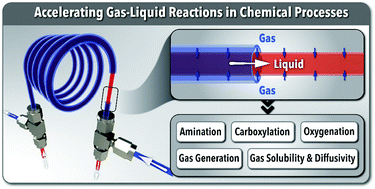
Over the past decade, continuous flow reactors have emerged as a powerful tool for accelerated fundamental and applied studies of gas–liquid reactions, offering facile gas delivery and process intensification. In particular, unique features of highly gas-permeable tubular membranes in flow reactors (i.e., tube-in-tube flow reactor configuration) have been exploited as (i) an efficient analytic tool for gas–liquid solubility and diffusivity measurements and (ii) reliable gas delivery/generation strategy, providing versatile adaptability for a wide range of gas–liquid processes. The tube-in-tube flow reactors have been successfully adopted for rapid exploration of a wide range of gas–liquid reactions (e.g., amination, carboxylation, carbonylation, hydrogenation, ethylenation, oxygenation) using gaseous species both as the reactant and the product, safely handling toxic and flammable gases or unstable intermediate compounds. In this highlight, we present an overview of recent developments in the utilization of such intensified flow reactors within modular flow chemistry platforms for different gas–liquid processes involving carbon dioxide, oxygen, and other gases. We provide a detailed step-by-step guideline for robust assembly and safe operation of tube-in-tube flow reactors. We also discuss the current challenges and potential future directions for further development and utilization of tubular membrane-based flow reactors for gas–liquid processes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...