Unique cellular interaction of macrophage-targeted liposomes potentiates anti-inflammatory activity†
Abstract
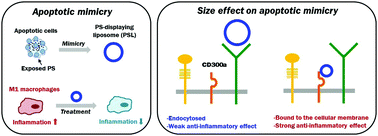
Nanomedicines that suppress macrophage-mediated chronic inflammation are important therapeutics for many inflammatory diseases. The small-sized (<100 nm) apoptotic-cell-mimetic macrophage-targeted liposomes served as a long-lasting immunosuppressive agent through preferential association with CD300a receptor, unlike larger liposomes, enabling the amelioration of hepatic inflammation in mice.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...