Surface modification effects of graphite for selective hydrogen absorption by titanium at room temperature†
Abstract
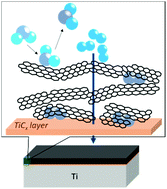
Surface modification effects of graphite and organic solvents on Ti were investigated by thermogravimetry (TG), Raman spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observations to improve its hydrogen absorption properties. As a result, Ti ball-milled with graphite showed high reactivity and selectivity for hydrogen with high durability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...