Polyamide nanofilms synthesized via controlled interfacial polymerization on a “jelly” surface†
Abstract
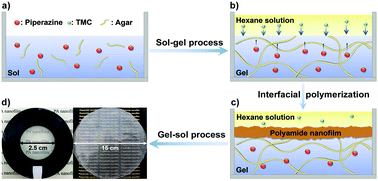
A thermal-sensitive “jelly” was used to control the diffusion of a diamine monomer for synthesizing polyamide free-standing nanofilms with an adjustable thickness of 5–35 nm. The reduced reaction rate of the interfacial polymerization at the hexane–“jelly” interface made the synthesized nanofilms show high water permeation flux and suitable salt rejection, and they also have highly negative surface charges and fairly smooth surfaces.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...