Design of a LiF-rich solid electrolyte interface layer through salt-additive chemistry for boosting fast-charging phosphorus-based lithium ion battery performance†
Abstract
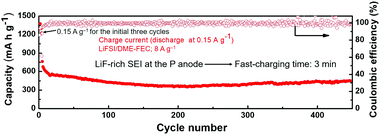
A robust and conductive LiF-rich solid electrolyte interface layer was generated at the phosphorus surface through salt-additive chemistry, and it then served as a high-performance fast-charging lithium ion battery anode, delivering a high reversible capacity of 450 mA h g−1 after 450 cycles with a high charging current density of 8 A g−1 (about 3 min).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...