In situ catalyst reactivation for enhancing alcohol electro-oxidation and coupled hydrogen generation†
Abstract
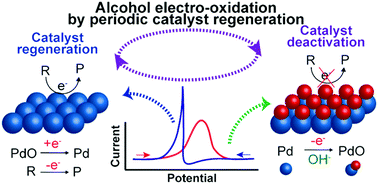
A novel method exploiting the in situ reactivation of a PdNi catalyst to enhance the electro-oxidation of alcohols is reported. The periodic regeneration of the catalyst surface leads to significant gains in terms of conversion rate, energy requirements and stability compared to the conventional potentiostatic method.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...