Cation–π binding ability of BN indole†
Abstract
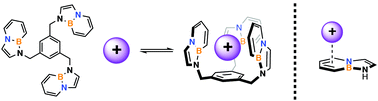
A BN indole-containing aromatic scaffold has been synthesized and the cation–π binding ability characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) monitored titrations. The resulting chemical shifts were analyzed using a non-linear curve fitting procedure and the extracted association constants (Ka's) compared with the natural indole scaffold. Computations were also performed to support our findings. This work shows that incorporation of a B–N bond in place of a C–C bond in an aromatic system slightly lowers the cation–π binding ability of the arene's π-system with simple cations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...