Solvent-driven migration of highly polar monomers into hydrophobic PDMS produces a thick graft layer via subsurface initiated ATRP for efficient antibiofouling†
Abstract
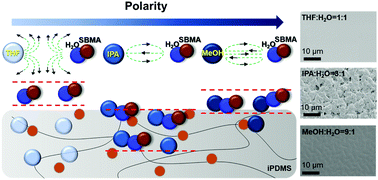
The sucessful grafting of highly polar polymer chains both on the surface and in the subsurface of PDMS via subsurface initiated ATRP for the improved antibiofouling performance is enabled by the diffusion of organic solvents (in a water-based binary solvent) which act as not only a “carrier” for hydrophilic monomers but also a “sweller” for the PDMS substrate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...