A highly sensitive signal-on biosensor for microRNA 142-3p based on the quenching of Ru(bpy)32+–TPA electrochemiluminescence by carbon dots and duplex specific nuclease-assisted target recycling amplification†
Abstract
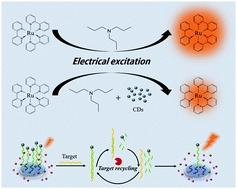
Carbon dots (CDs) have been used to quench the electrochemiluminescence (ECL) of a Ru(bpy)32+–tripropylamine (TPA) system for the first time. In addition, this phenomenon has been coupled with duplex specific nuclease-assisted target recycling amplification to develop a highly sensitive ECL biosensor for microRNA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...