Efficient 125I-radiolabeling of biomolecules using a strain-promoted oxidation-controlled cyclooctyne–1,2-quinone cycloaddition reaction†
Abstract
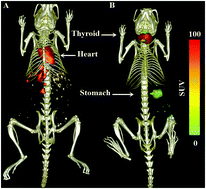
We report a novel 1,2-catechol based radioiodinated precursor for radioiodination of bicyclo[6.1.0]nonyne (BCN) installed biologically active molecules using a strain-promoted oxidation-controlled cyclooctyne–1,2-quinone cycloaddition reaction (SPOCQ) under ambient conditions. Compared to the reported methodologies, the new strategy demonstrates some clear advantages, including high in vitro and in vivo stability, high radiochemical yield, and exceptionally fast reaction kinetics at micro-molar concentration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...