A stimuli-responsive anticancer drug delivery system with inherent antibacterial activities†
Abstract
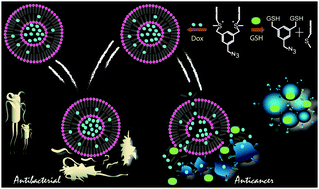
We describe a novel class of stimuli-sensitive sulfonium-based synthetic lipids, which exhibit several favorable biophysical properties of phospholipids. The potent sulfonium-based lipid was successfully disassembled by glutathione to release the encapsulated drug molecules in a controlled manner. The cationic lipid also showed lower cytotoxicity against mammalian cells and displayed moderate antibacterial activities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...