Impacts on carbon dioxide electroreduction of cadmium sulfides via continuous surface sulfur vacancy engineering†
Abstract
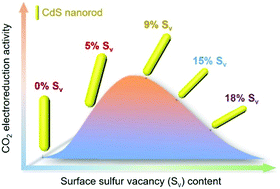
Cadmium sulfide (CdS) has been found to be a favorable electrocatalyst for CO2 reduction owing to its appropriate binding energy of the key intermediates that originate from the CdS(002) surface with S vacancy (Sv). In this work, CdS nanorods with a medium Sv content (ca. 9%) give the highest CO Faraday efficiency of 100 ± 0.5% and a partial current density of −20.5 ± 0.2 mA cm−2.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...