Cyclam-based antibacterial molecules eradicate Gram-negative superbugs with potent efficacy against human corneal infection†
Abstract
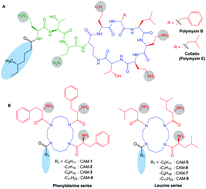
Cyclam-based antibacterial molecules (CAMs) that display potent activity against both the planktonic and stationary phase of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria were rationally designed. The optimized compound retained its activity in human plasma and eradicated preformed biofilms. It also revealed excellent potency in an ex vivo model of human corneal infections with negligible propensity of resistance development. This indicated the potential of this class of compound as a future antibacterial agent to tackle human corneal infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...