An ‘on-demand’ photothermal antibiotic release cryogel patch: evaluation of efficacy on an ex vivo model for skin wound infection†
Abstract
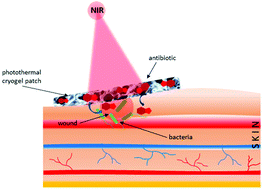
A myriad of topical therapies and dressings are available to the clinicians for wound healing skin, but only a very few have shown their effectiveness in promoting wound repair due to challenges in controlling drug release. To address this issue, in this work, a near infrared (NIR)-light activable cryogel based on butyl methacrylate (BuMA) and poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate (PEGMEMA) incorporated with reduced graphene oxide (rGO) was fabricated. The obtained cryogel provides the required hydrophilicity beneficial for wound treatment. The excellent photo-thermal properties of rGO allow for heating the cryogel, which results in subsequent swelling of the cryogel (CG) followed by release of the encapsulated drug load, cefepime in our case. Without photothermal activation, no release of payload was observed. The potential of this bandage for wound healing was examined using an ex vivo human skin model infected with Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). Apart from the efficacy of the cryogel based wound healing system, our results also suggest that the ex vivo wound model evaluated here provides a rapid and valuable tool to study superficial skin infections in humans and test the efficacy of antimicrobial agents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...