A novel injectable pH–temperature sensitive hydrogel containing chitosan–insulin electrosprayed nanosphere composite for an insulin delivery system in type I diabetes treatment†
Abstract
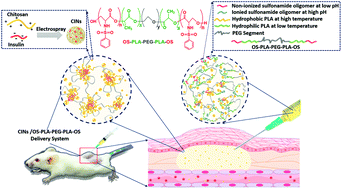
A novel insulin composite delivery system was prepared and characterized. The composite consisted of a pH- and temperature-sensitive hydrogel, which is an oligomer serine-b-poly(lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(lactide)-b-oligomer serine (OS-PLA-PEG-PLA-OS) pentablock copolymer, as matrix and chitosan–insulin electrosprayed nanospheres (CIN) as constituent materials. The properties of the OS-PLA-PEG-PLA-OS pentablock copolymer and the chitosan–insulin nanoparticles were characterized. The chitosan–insulin nanospheres uniformly distributed in the matrix had a reinforcing effect on the mechanical properties and prolonged the degradation time of the hydrogel depot under body conditions. The composite solutions accommodating different concentrations of the chitosan–insulin nanospheres were subcutaneously injected into induced diabetic BALB/c mice to study the in vivo insulin-release profile. The result showed that insulin concentrations in blood plasma were maintained at a steady-state level. Furthermore, the bio-properties of the insulin were retained and it showed a blood glucose level reducing effect for more than 60 hours after injection to a streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mouse model. The results suggested that this injectable pH–temperature sensitive hydrogel containing chitosan–insulin electrosprayed nanosphere composites has promising potential applications for type 1 diabetes treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...