Bioreducible, branched poly(β-amino ester)s mediate anti-inflammatory ICAM-1 siRNA delivery against myocardial ischemia reperfusion (IR) injury†
Abstract
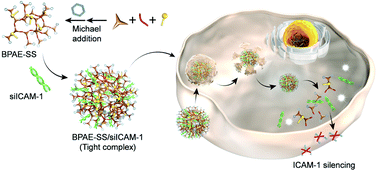
siRNA-mediated RNA interference (RNAi) against inflammation-related genes provides a promising modality for the treatment of myocardial ischemia reperfusion (IR) injury, and its success is critically dependent on the development of efficient yet safe siRNA delivery vehicles. Herein, we developed a bioreducible, branched poly(β-amino ester) with built-in redox-responsive domains (BPAE-SS) for the effective ICAM-1 siRNA delivery into injured rat cardiac microvascular endothelial cells (RCMECs). The branched BPAE-SS with a multivalent structure afforded potent siRNA binding affinity compared to its linear analogue, while upon internalization into RCMECs it was instantaneously degraded by intracellular glutathione (GSH) into small segments to mediate “on-demand” siRNA release and diminish the toxicity of post-transfection materials. By synchronizingly overcoming these critical barriers, BPAE-SS mediated remarkable ICAM-1 knockdown in IR-injured rats at 400 μg siRNA per kg via single i.v. injection, and subsequently suppressed myocardial inflammation, apoptosis, and fibrosis to recover the cardiac function. This study therefore provides a unique delivery system that can address the multiple critical challenges against non-viral siRNA delivery, and the potent therapeutic efficacy of BPAE-SS-mediated ICAM-1 silencing provides a promising strategy for the anti-inflammatory treatment of myocardial IR injury.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...