Bioinorganic supplementation of calcium phosphate-based bone substitutes to improve in vivo performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies†
Abstract
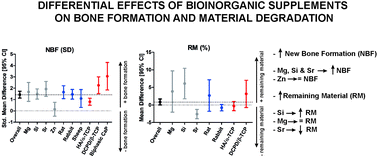
Supplementation of CaP-based bone graft substitutes with bioinorganics such as strontium, zinc or silicon is an interesting approach to increase the biological performance in terms of bone regenerative potential of calcium phosphate (CaP)-based bone substitutes. However, the in vivo efficacy of this approach has not been systematically analyzed, yet. Consequently, we performed a systematic review using the available literature regarding the effect of bioinorganic supplementation in CaP-based biomaterials on new bone formation and material degradation in preclinical animal bone defect models and studied this effect quantitatively by performing a meta-analysis. Additional subgroup analyses were used to study the effect of different bioinorganics, animal model, or phase category of CaP-based biomaterial on bone formation or material degradation. Results show that bioinorganic supplementation increases new bone formation (standardized mean difference [SMD]: 1.43 SD, confidence interval [CI]: 1.13–1.73). Additional subgroup analysis showed that strontium, magnesium and silica significantly enhanced bone formation, while zinc did not have any effect. This effect of bioinorganic supplementation on new bone formation was stronger for DCPD or β-TCP and biphasic CaPs than for HA or α-TCP (p < 0.001). In general, material degradation was slightly hindered by bioinorganic supplementation (mean difference [MD]: 0.84%, CI: 0.01–1.66), with the exception of strontium that significantly enhanced degradation. Overall, bioinorganic supplementation represents an effective approach to enhance the biological performance of CaP-based bone substitutes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...