A disulfide based low molecular weight gel for the selective sustained release of biomolecules†
Abstract
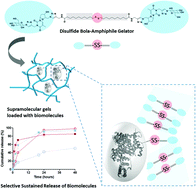
Constructing biocompatible soft materials via supramolecular approaches remains an important challenge for in vivo applications. Substantial efforts have been made to develop biocompatible non-polymeric materials allowing sustained release of biomolecules and/or drugs in vivo. Herein, we introduce disulfide based low molecular weight gels (LMWGs) allowing the in vitro selective sustained release of proteins containing thiol residues. The novel glycosylated nucleoside based bola-amphiphile (GNBA), which features a disulfide bond inserted in the hydrophobic segment, self-assembles to stabilize the resulting hydrogel. Rheological studies show the dominant elastic character and thixotropic properties of the disulfide LMWG demonstrating its injectability. In vitro and in vivo biodegradation investigations reveal that the disulfide LMWG is stable for several weeks. Importantly, disulfide bonds can be cleaved through the thiol-disulfide exchange reactions with small redox molecules such as dithiothreitol (DTT). The disulfide LMWG loaded with a thiol-containing protein (bovine serum albumin) features sustained release in vitro, whereas a dextran of the same molecular weight, lacking a thiol biomolecule, shows quick release. The disulfide GNBA is the first example of a LMWG allowing selective long term sustained release in vitro via a disulfide reshuffling mechanism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...