Modulating neutrophil extracellular traps for wound healing†
Abstract
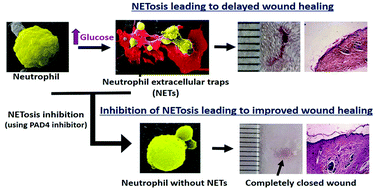
A diabetic microenvironment primes neutrophils for NETosis, a process of formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) that further degrades the neutrophils and makes them unavailable for the early-stage inflammatory processes. Mechanistically, simple modification of arginine residues of histones to citrulline by peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD4) enzyme is considered to be a prerequisite for NETosis. In fact, under diabetic conditions, an increase in PAD4-mediated NET formation is considered as one of the reasons for impaired wound healing. Therefore, in the present work, an alginate-GelMa (generally recognized as safe category by FDA, USA) based hydrogel scaffold containing a tripeptide (Thr-Asp-F-amidine) that inhibits PAD4 is developed, based on the hypothesis that inhibiting PAD4 enzyme might offer a way to enhance wound healing under diabetic conditions. The scaffolds are thoroughly characterized for their physicochemical and biological properties. Furthermore, neutrophil–scaffold interactions in terms of NETosis ability and release of other related biomarkers are studied. The wound healing ability is evaluated by a cell migration assay. In vivo wound healing efficacy of the developed scaffolds is demonstrated using a diabetic rat model. The results suggest a reduction in NETosis in the presence of a PAD4 inhibitor. Thus, the study demonstrates a novel scaffold system to deliver the PAD4 inhibitor that can be used to modulate NETosis and improve wound healing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...