“Swiss roll”-like bioactive hybrid scaffolds for promoting bone tissue ingrowth and tendon-bone healing after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction†
Abstract
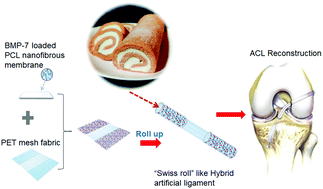
The choice of grafts for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction is a critical issue in sports medicine. Previous studies have revealed that scaffolds prepared from a single material could not achieve complete integration between the graft and autogenous bone tunnel. To solve this problem, we hypothesize that combining degradable scaffolds with nondegradable scaffolds can produce a novel hybrid ligament with the advantages of both types of scaffolds. In this study, a bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP-7)-loaded polycaprolactone (PCL) nanofibrous membrane was first manufactured as the degradable part of the hybrid ligament by using layer-by-layer (LbL) self-assembly. Then, we fabricated a multifunctional novel hybrid ligament by rolling up this nanofibrous membrane and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) mesh fabric (nondegradable part) into a “swiss roll” structure. The in vitro experimental results showed that this hybrid ligament could significantly improve the biocompatibility of pure PET ligament and further promote cell mineralization. The in vivo experimental results showed that this unique structure significantly promoted the integration of hybrid ligaments and bone tunnels, thereby achieving real “ligamentization” after ACL reconstruction surgery. These results suggest that this novel hybrid biomimetic artificial ligament scaffold provides a new direction for graft selection for ACL reconstruction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...