Hyaluronic acid hydrophilic surface rehabilitating curcumin nanocrystals for targeted breast cancer treatment with prolonged biodistribution†
Abstract
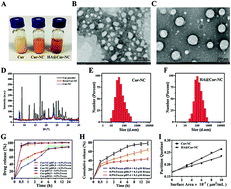
Due to its high therapeutic efficiency and low systemic toxicity, natural bioactive curcumin has attracted more and more attention as a potential antineoplastic drug. Although the emergence of a carrier-free nanocrystalline technology could improve the solubility and guarantee the high drug loading of curcumin, uncontrollable drug release and fast systemic metabolism are definite obstacles that hinder its further application in cancer treatment. Here, hyaluronic acid (HA) modification was carried out on the surface of curcumin nanocrystals (Cur-NC) to obtain surface reformed hydrophilic HA@Cur-NCs that exhibit prolonged biodistribution. Besides this, HA@Cur-NC shows enhanced intracellular uptake in CD44 overexpressing MDA-MB-231 cells, but reduced uptake when pre-treated with HA. The apoptotic effects, confirmed by flow cytometry, suggest that HA@Cur-NC could achieve high anticancer activity against MDA-MB-231 cells. In vivo pharmacokinetic studies suggest that the t1/2 and mean residence time (MRT) of Cur are significantly extended after the intravenous administration of HA@Cur-NC in normal rats. Moreover, HA@Cur-NC demonstrated superior anticancer effects in a murine 4T1 orthotopic breast cancer model compared with free drug and Cur-NC. Overall, these results show the potential of HA@Cur-NC as a suitable formula for use in breast cancer therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...