Rapid and highly sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium in lettuce by using magnetic fluorescent nanoparticles†
Abstract
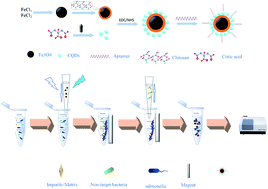
The highly efficient detection of Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium), a common foodborne bacterial, is important for the safety assurance of leafy vegetables. In this study, a fluorescent sensor (FMNCs-Apt), based on Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and aptamer-modified carbon quantum dots, was developed for the rapid and highly sensitive detection of S. typhimurium in lettuce. First, carbon quantum dots were covalently bonded to the surface of prepared Fe3O4@chitosan to form magnetic fluorescence composite nanoparticles (FMNCs). Then, the aptamers of S. typhimurium were covalently linked to the surface (and named FMNCs-Apt). Fluorescence intensity of the FMNCs-Apt probes decreased as they aggregated on the surface of the bacteria, and the aggregation was separated using a magnet. Under the optimal conditions, the fluorescence change values of the solution showed a good linear relationship with the concentration of Salmonella (103–106 CFU mL−1). The detection limit of the method is 100 CFU mL−1 and 138 CFU mL−1 in fresh-cut vegetable washing solution and lettuce sample, respectively. Accordingly, this developed fluorescent probe became a highly sensitive and efficient sensor for the rapid detection of S. typhimurium in lettuce.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...