Selective and simultaneous sensing of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid based on nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon†
Abstract
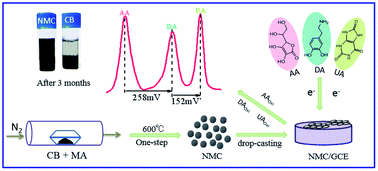
Development of novel sensing nanostructures for facile, economical and fast applications has attracted more and more interest. Herein, a nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon (NMC) was synthesized by pyrolyzing a mixture of melamine and carbon black at a low-temperature (600 °C) and exploited for the simultaneous sensing of ascorbic acid (AA), dopamine (DA) and uric acid (UA). The as-made NMC exhibits a rougher surface and smaller size than carbon black. Such a one-pot method is very versatile, quick and inexpensive, easy to handle (solvent-, catalyst-, and template-free) and scalable. The oxidation potentials of the NMC/GCE negatively shift and the current responses are enhanced greatly towards the oxidation of AA, DA and UA thanks to the large surface area, mesoporous structure and N-doped active sites. The peak to peak potential separations are 258 and 410 mV for AA–DA and AA–UA. The linear ranges of AA, DA and UA are 5–4500 μM, 0.005–35 μM and 0.5–3500 μM, respectively, and their detection limits are 0.15 μM (AA), 1.6 nM (DA) and 0.15 μM (UA). Meanwhile, the NMC/GCE exhibits satisfactory stability and anti-interference ability. These results show that NMC could be a promising candidate material for electrochemical sensor construction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...