Sensitive detection of microRNA using QCM biosensors: sandwich hybridization and signal amplification by TiO2 nanoparticles
Abstract
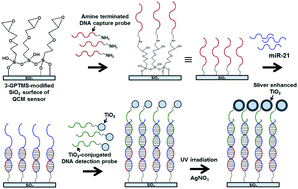
MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) is known to act as an important biomarker for cancer, in that its up-regulation is closely related to several types of malignant tumor. Sensitive and accurate detection of miR-21 using a biosensor is highly challenging. In this study, sensitive and selective detection technology for miR-21 molecules using a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) biosensor was developed. Sandwich hybridization between miR-21 and specially designed probes and a subsequent TiO2 photocatalytic silver enhancement reaction were the driving forces for sensitive detection with high selectivity for miR-21. Using this strategic approach under optimal conditions, the novel QCM biosensor can detect miR-21 with a LOD of 0.87 pM over the entire linear range from 0.1 pM to 10 μM, with a correlation coefficient of 0.988. In addition, the developed QCM biosensor was very effective in the quantification of miR-21 in serum samples, so the proposed miRNA detection method offers great potential for the diagnosis of early disease, such as cancer and vascular diseases, and could be an excellent alternative for biological research and clinical diagnosis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...