Adsorptive removal of Hg2+ from environmental water samples using thioglycerol-intercalated magnetic layered double hydroxides
Abstract
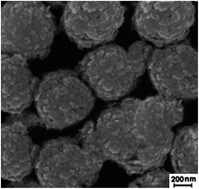
Herein, the removal of Hg2+ from environmental water samples was carried out using a novel nanoadsorbent based on magnetite nanoparticles coated by a thioglycerol-intercalated layered double hydroxide. The prepared material was characterized using scanning electron microscopy equipped with an energy dispersive X-ray analyzer and Fourier transform infrared spectrometry. The effective parameters of the removal procedure were identified and optimized through the one-variable-at-a-time method. Under the optimal conditions, the removal characteristics of the synthesized adsorbent including selectivity, distribution coefficient, and loading capacity were calculated in the presence of some interfering ions. The removal efficiency of 94.98% together with the distribution coefficient of 5.00 × 105 mL g−1 and loading capacity of 480.69 mg g−1 showed the considerable capability of this novel adsorbent in the selective removal of Hg2+ from aqueous samples. To evaluate the performance of the synthesized adsorbent in the removal of Hg2+ from environmental water samples, the removal of the desired analyte was carried out using four different real samples. The removal procedures were conducted at the analyte concentration levels of 10.0 and 50.0 mg L−1 for each aqueous sample. The obtained results showed that the removal efficiency was in the range of 91.99–94.97%, which confirmed the high performance of the synthesized adsorbent in the removal of Hg2+ from real samples. Furthermore, the relative standard deviation of as low as 4.18–6.17% showed the acceptable repeatability of this method.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...