A perylene diimide-based near-IR ratiometric sensor for detection of Cu2+ ions: ensemble for discrimination of CN− and S2− ions†
Abstract
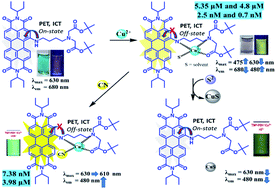
In this study, we have designed and synthesized a perylene diimide-based novel chromo-fluorescent chemosensor (TBP-PDI), which shows selective ratiometric fluorescent ‘turn-on’ (F482/F680 nm) and colorimetric (A476/A630) responses on addition of Cu2+ ions in a HEPES buffer : CH3CN (4 : 6, v/v, pH 7.2) medium and CH3CN. The detection limits of TBP-PDI for Cu2+ were found to be 4.8 μM/2.5 nM using fluorescence mode and 5.22 μM/0.71 nM using absorbance mode in these solvents, respectively. The complexation of TBP-PDI with Cu2+ was further supported by NMR, dynamic light scattering (DLS), cyclic voltammetric (CV) and differential pulse voltammetric (DPV) studies. The limit of detection for Cu2+ using DPV is 0.46 μM. This perylene diimide–Cu2+ based ensemble (TBP-PDI–Cu2+) was further used as a ‘turn-on’ type chemosensor for CN− ions with a detection limit of 7.38 nM/3.98 μM and as a ‘turn-off’ type chemosensor for S2− with a detection limit of 35 μM. These changes can be explained by the fact that CN− interacts with the TBP-PDI–Cu2+ ensemble through coordination with Cu2+via displacement of solvent molecules whereas S2− interacts with the TBP-PDI–Cu2+ ensemble via sequestration of Cu2+ from the binding pocket of the ensemble.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...