A deep learning approach to identify association of disease–gene using information of disease symptoms and protein sequences†
Abstract
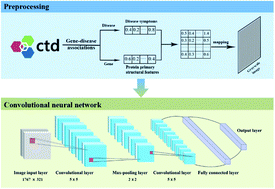
Identifying the association of disease–gene is one of the significant steps in understanding pathogenesis and discovering therapeutic targets. Symptoms of disease and sequences of protein are important resources for recognizing the relationship between disease and gene. This study provides a new method for identifying disease-associated genes. In the meantime, symptomatic information and primary structural features are utilized to characterize disease and protein, respectively. A grayscale image is adopted to represent disease–gene association. A convolutional neural network is employed to construct a model for identifying potential disease-associated genes. The accuracy and sensitivity of the training set are 92.38% and 91.17%, respectively, and those of the test set are 80.64% and 80.69%, respectively. Furthermore, predicted potential genes are supported by access to the literature and databases as well as enrichment analysis, demonstrating that the current method can be effectively used for the prediction of disease genes. The source code of Matlab is freely available on request to the authors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...