Vacuum-assisted electrokinetic supercharging in flow-gated capillary electrophoresis for rapid analysis of high-salt cerebrospinal fluid samples
Abstract
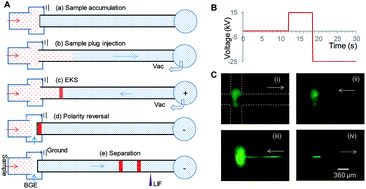
On-line sample preconcentration is often required to achieve sensitive detection of specific analytes in capillary electrophoresis. However, available on-line techniques for concentrating high-salt samples such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are mainly limited to sweeping and dynamic pH-junctions, etc. Electrokinetic supercharging (EKS) for sample preconcentration combines the techniques of field-amplified sample injection and transient isotachophoresis that may generate tremendous signal enhancement while maintaining high separation efficiency. This paper reports a novel EKS method for the on-line preconcentration of high-salt CSF samples in flow-gated capillary electrophoresis. The basic procedures include three major steps. First, a sample plug was hydrodynamically injected under vacuum; second, a voltage with the reversed polarity was applied to perform EKS with the assistance of a vacuum during the sample plug push-out; and finally a normal-polarity voltage was applied for separation. Specifically, amino acids were fluorogenically derivatized with naphthalene-2,3-dicarboxaldehyde (NDA) in the presence of cyanide. The optimal final sample medium included 20% CSF (or aCSF in volume), 50% acetonitrile, 12.0 mM borate, 5.0 mM KCN, 5.0 mM NDA, and 2.0 mM EDTA; and the separation buffer was composed of 40.0 tetraborate pH 9.2, 50.0 mM SDS, and 3.5 mM hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. The enhancement factors for a series of amines were in the range of 30–100 fold, and the detection limits were estimated to be below 0.10 nM. The developed method was coupled with alternate injections for the one-point standard addition method to determine γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in CSF from rat brain striatum. The results demonstrated detection sensitivity and accuracy for the rapid analysis of high-salt CSF samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...