A novel method for simultaneously screening superoxide anion scavengers and xanthine oxidase inhibitors using hydroethidine as a fluorescent probe coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry†
Abstract
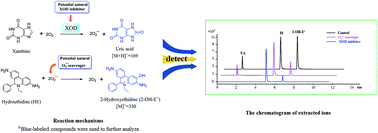
Excess reactive oxygen species can cause cellular damage, and are involved in many pathological processes such as inflammation, atherosclerosis and cancer. Reactive oxygen species can be generated by several mechanisms, one of which involves the reaction of xanthine oxidase with xanthine to generate a superoxide anion and uric acid. In this study, a new method using hydroethidine as a fluorescent probe coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) was developed for simultaneously screening xanthine oxidase inhibitors and superoxide anion scavengers. This method was validated using the known superoxide anion radical scavenger L-ascorbic acid and the xanthine oxidase inhibitor febuxostat. As a result, six compounds, including salvianolic acid C, quercetin, apigenin, α-tocopherol, formononetin and aloin, were successfully screened by this method. Compared with traditional colorimetric methods, the developed method was sensitive, accurate and fast. This work demonstrated that the developed fluorescent probe coupled with HPLC-MS method was effective for simultaneously screening xanthine oxidase inhibitors and superoxide anion radical scavengers from natural product libraries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...