SPE cartridges with a 3D graphene framework for extraction of triclosan in environmental water†
Abstract
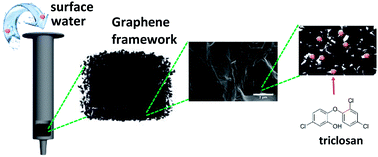
Pharmaceuticals and personal care products containing triclosan, an antibacterial agent, have been used in large amounts, resulting in contamination for humans and non-target organisms. In this work, we present an efficient 3D graphene filled solid-phase extraction (SPE) cartridge, obtained by a single reduction step of graphene oxide. The morphological, structural and compositional characterization of the 3D graphene framework was carried out by scanning electron microscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The results show a 3D framework with cavities, which was efficiently applied as a sorbent in extraction–elution assays of triclosan in an aqueous matrix. The efficiencies were calculated after experiments with a high performance liquid chromatograph coupled with an ultraviolet-visible detector. Reproducible high extraction and elution efficiencies were achieved (ca. 100% and ca. 98%, respectively) for a relatively low amount of sorbent (40 mg). When applied for the analysis of surface water from a Brazilian lake (Guaíba), the 3D graphene framework extracted ca. 68% of triclosan, presenting an elution of ca. 98%. Compared to commercial sorbents, the material synthesized in this work presents advantages in terms of the simple methodology for preparation, low amount of sorbent required in the cartridge to achieve high efficiencies and enrichment factor of eight times in the loading volume.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...