Boronate affinity material-based sensors for recognition and detection of glycoproteins
Abstract
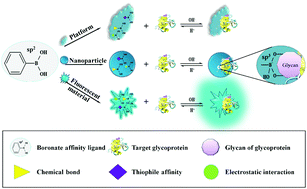
Glycoproteins are closely linked to the occurrence and development of many diseases. Therefore, it is of great importance to develop highly selective, sensitive, efficient detection methods for glycoproteins. To overcome the problems with traditional detections methods, such as mass spectrometry, chromatography-mass spectrometry, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, boronate affinity material (BAM)-based sensors have developed rapidly for the specific recognition and detection of glycoproteins because of the advantages of pH-controlled binding/release, reversibility of the reaction, high specificity, and high selectivity, showing their wide application prospects. In recent years, there have been many significant leaps in the use of BAMs for sensing and detecting glycoproteins, but there are still many challenges and room for development. Therefore, this review critically investigates and summarizes recent advances with BAM-based sensors for glycoprotein detection. We focus on the common boronate affinity ligands of BAMs and their grafting methods, functional materials utilized in the synthesis of BAM-based sensors, advanced technologies, and applications. Finally, we propose the remaining challenges and future perspectives to accelerate the development of BAMs, and to utilize it for further developing versatile BAMs with a variety of promising applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...