Genetically encoded biosensors for the detection of rapamycin: toward the screening of agonists and antagonists†
Abstract
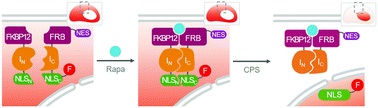
Biosensors are valuable tools for the rapid screening of biological targets with high sensitivity and specificity. It is important to screen biological events in their native context for pharmacological and toxicological applications. However, in vitro biosensors often require purified probes and targets for screening, thus providing limited information on the biological activities of targets in their native environment. To address this issue, we developed a cell-based sensing system that could detect a biologically active small molecule, rapamycin (Rapa). We designed a reporter system based on fluorescence translocation by signal peptide reconstitution. Herein, signal peptides are activated by conditional protein splicing without the need for refolding into a functional tertiary structure, thus eliminating false positives and negatives due to mere binding or misfolding. The developed biosensor demonstrated excellent sensitivity with a limit of detection of 0.1 nM, and it was able to screen the agonist and antagonist of Rapa. The developed cell-based sensing system could contribute to improving the screening system aimed to identify the natural mimetics of Rapa and potential drug candidates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...