Low frequency stimulation induces polarization-based capturing of normal, cancerous and white blood cells: a new separation method for circulating tumor cell enrichment or phenotypic cell sorting†
Abstract
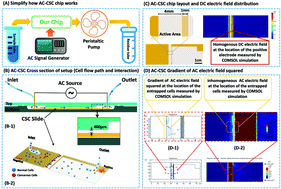
Separation of cancerous from normal cells is of broad importance in a large number of cancer diagnosis and treatment methods. One of the most important factors to designate and specify different cells is to study their dielectric and electric cell membrane characteristics. In this research, a label-free cytological slide chip (CSC) is designed and fabricated based on AC electric field stimulation of breast cell lines and blood cells at low frequencies (1 kHz–200 kHz). The AC-CSC traps cells based on their dielectric polarization functions which is distinct between different phenotypes of breast cells and blood cells. We learned that by using AC electric fields, each breast cell line shows a capturing response to a specific range of frequencies. The progression in cancer phenotypes decreases the cell's polarizability. Hence, characteristic frequency responses were achieved for these cells. In this study, thermal potential and electrolysis which were the main bottle neck problems in DC applied fields were completely solved. The AC-CSC could be used in CTC separation from leukocytes, a test performed based on a compound with 1% cancer cells in white blood cells (1% MDA-MB-231 : 99% WBC) which results in 90% capturing efficiency of cancer cells. Frequency dependent capturing brings so much hope that smart slides will be useful at the clinical stage in the near future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...