A magneto-fluorescence bacteria assay strategy based on dual colour sulfide fluorescent nanoparticles with high near-IR conversion efficiency†
Abstract
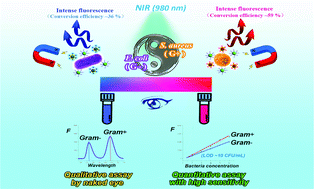
Anti-Stokes fluorescence induced by near-IR (NIR) radiation is particularly advantageous for the bioassay of complex samples, but most of the commonly used NIR-induced fluorescence nanomaterials such as up-conversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) do not exhibit satisfactory fluorescence intensity and work against achieving a highly sensitive bioassay. In this study, we a construct sensitive and specific bacteria biosensor based on the NIR-stimulated CaS: Eu, Sm, Mn and SrS: Ce, Sm, Mn nanoparticles. The fluorescent nanoparticles are conjugated with bacteria recognition fragments. In addition, the independent emission bands of these two types of fluorescent nanoparticles make it possible to detect and quantify Gram-positive strain and Gram-negative strain, simultaneously. Intense fluorescence and magnetic enrichment of magneto-fluorescence systems enable bacteria discrimination with the naked eye and improve sensitivity in trace bacteria detection (<20 CFU mL−1). The linear relationship between the fluorescence intensity and bacterial concentration is established with a detection range of 25–106 CFU mL−1. Furthermore, this NIR-excited assay strategy demonstrates better anti-interference capability than UV/visible-excited assay methods, showing high potential and practical value for medical diagnostics and bacteria monitoring.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...