Phosphorylcholine-based encoded hydrogel microparticles with enhanced fouling resistance for multiplex immunoassays†
Abstract
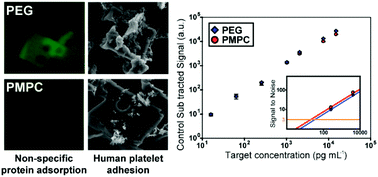
Due to the growing interest in multiplex protein detection, encoded hydrogel microparticles have received attention as a possible path to high performance multiplex immunoassays through a combination of high multiplexing capability and enhanced binding kinetics. However, their practical operation in real complex samples is still limited because polyethylene glycol, which is the main component of hydrogel particles, suffers from oxidative damage and relatively high fouling properties in biochemical solutions. Here, we introduce poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) (PMPC)-based encoded hydrogel microparticles to perform fouling-resistant multiplex immunoassays, where the anti-fouling characteristics are attributed to the zwitterionic PMPC. By applying a newly developed molding lithography technique, viscous PMPCs with low reactivity were successfully incorporated into the hydrogel network while maintaining uniformity and rigidity for use in multiplex immunoassays. Non-specific protein adsorption on the PMPC particles was reduced by about 37.5% compared to that of conventional PEG particles, which leads to better assay sensitivity. We also validate the multiplex capability of the PMPC particles by performing multiplex detection of two target proteins. Furthermore, we verify that the PMPC particles have a 70% enhancement in anti-fouling characteristics compared to PEG particles in human platelet-rich plasma, potentiating a practical immunoassay platform for clinical diagnosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...