Rapid detection of 21 β-lactams using an immunochromatographic assay based on the mutant BlaR-CTD protein from Bacillus Licheniformis†
Abstract
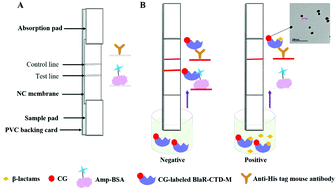
In this study, a gold immunochromatographic assay (GICA) based on a penicillin receptor protein (PBP) is proposed to simultaneously detect penicillin, cephalosporin, and carbapenem antibiotics in milk and chicken. A mutant PBP, carboxy-terminal of the β-lactam sensor-transducer protein (BlaR-CTD, I188KS19CG24C) from Bacillus licheniformis ATCC14580 was expressed in E. coli as a soluble His-tag fusion protein. The purified BlaR-CTD mutant was labeled with colloidal gold (CG-BlaR-CTD-M) and applied to develop GICA. The GICA method was performed based on a competitive form, where the binding of the ampicillin-bovine serum albumin conjugate (Amp-BSA) to CG-BlaR-CTD-M was inhibited by free β-lactams in samples. The performance of the assay was confirmed by analysis of milk and chicken samples. The limits of detection of 21 β-lactam antibiotics met the maximum residue limits set by the European Union and China. The GICA gave results within 10 min, thus providing a rapid and reliable method for the on-site detection of multiple β-lactams in milk and chicken samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...