An electrochemical sensor based on enzyme-free recycling amplification for sensitive and specific detection of miRNAs from cancer cells†
Abstract
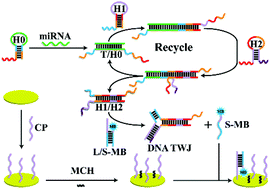
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are desirable targets for the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of diverse human diseases. In this study, we developed a universal and enzyme-free signal amplification approach for the quick, sensitive and specific electrochemical detection of diverse miRNAs from tumor cells using a catalyzed hairpin assembly (CHA) and the DNA three-way junction (DNA TWJ). The target miRNA, which was formed as an initiator through specific recognition, periodically triggered the assembly of two hairpins into a duplex via CHA. Subsequently, these duplexes induced the catalytic assembly of the DNA three-way junction and the release of the methylene blue-labeled DNA strand S (S-MB). Thereafter, the S-MB was captured using the electrode through hybridization with the capture probe to generate a notable current response. The proposed biosensor could be switched in response to different miRNA targets by changing the specific sequence of H0. These findings indicate its ability to distinguish single base mismatch miRNAs and analyze miRNAs extracted from cells. Therefore, the universal and enzyme-free signal amplified electrochemical method described herein can be potentially useful in diverse miRNA-related clinical analysis and disease diagnosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...