Plasmonic nanobiosensors for detection of microRNA cancer biomarkers in clinical samples†
Abstract
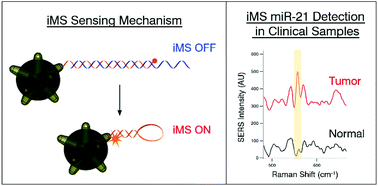
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play an important role in the regulation of biological processes and have demonstrated great potential as biomarkers for the early detection of various diseases, including esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) and Barrett's esophagus (BE), the premalignant metaplasia associated with EAC. Herein, we demonstrate the direct detection of the esophageal cancer biomarker, miR-21, in RNA extracted from 17 endoscopic tissue biopsies using the nanophotonics technology our group has developed, termed the inverse molecular sentinel (iMS) nanobiosensor, with surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) detection. The potential of this label-free, homogeneous biosensor for cancer diagnosis without the need for target amplification was demonstrated by discriminating esophageal cancer and Barrett's esophagus from normal tissue with notable diagnostic accuracy. This work establishes the potential of the iMS nanobiosensor for cancer diagnostics via miRNA detection in clinical samples without the need for target amplification, validating the potential of this assay as part of a new diagnostic strategy. Combining miRNA diagnostics with the nanophotonics technology will result in a paradigm shift in achieving a general molecular analysis tool that has widespread applicability for cancer research as well as detection of cancer. We anticipate further development of this technique for future use in point-of-care testing as an alternative to histopathological diagnosis as our method provides a quick result following RNA isolation, allowing for timely treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...