Profiling of immune–cancer interactions at the single-cell level using a microfluidic well array†
Abstract
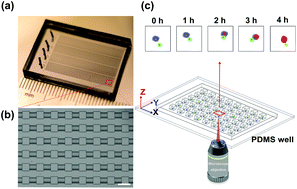
Cancer immunotherapy has achieved great success in hematological cancers. However, immune cells are a highly heterogeneous population and can vary highly in clonal expansion, migration and function status, making it difficult to evaluate and predict patient response to immune therapy. Conventional technologies only yield information on the average population information of the treatment, masking the heterogeneity of the individual T cell activation status, the formation of immune synapse, as well as the efficacy of tumor cell killing at the single-cell level. To fully interrogate these single-cell events in detail, herein, we present a microfluidic microwell array device that enables the massive parallel analysis of the immunocyte's heterogeneity upon its interaction pairs with tumor cells at the single-cell level. By precisely controlling the number and ratio of tumor cells and T cells, our technique can interrogate the dynamics of the CD8+ T cell and leukemia cell interaction inside 6400 microfluidic wells simultaneously. We have demonstrated that by investigating the interactions of T cell and tumor cell pairs at the single-cell level using our microfluidic chip, details hidden in bulk investigations, such as heterogeneity in T cell killing capacity, time-dependent killing dynamics, as well as drug treatment-induced dynamic shifts, can be revealed. This method opens up avenues to investigate the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy and resistance at the single-cell level and can explore our understanding of fundamental cancer immunity as well as determine cancer immunotherapy efficacy for personalized therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...