Trace manganese detection via differential pulse cathodic stripping voltammetry using disposable electrodes: additively manufactured nanographite electrochemical sensing platforms†
Abstract
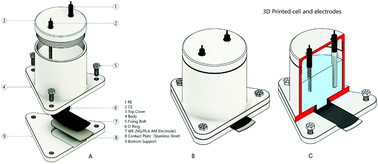
Additive manufacturing is a promising technology for the rapid and economical fabrication of portable electroanalytical devices. In this paper we seek to determine how our bespoke additive manufacturing feedstocks act as the basis of an electrochemical sensing platform towards the sensing of manganese(II) via differential pulse cathodic stripping voltammetry (DPCSV), despite the electrode comprising only 25 wt% nanographite and 75 wt% plastic (polylactic acid). The Additive Manufactured electrodes (AM-electrodes) are also critically compared to graphite screen-printed macroelectrodes (SPEs) and both are explored in model and real tap-water samples. Using optimized DPCSV conditions at pH 6.0, the analytical outputs using the AM-electrodes are as follows: limit of detection, 1.6 × 10−9 mol L−1 (0.09 μg L−1); analytical sensitivity, 3.4 μA V μmol−1 L; linear range, 9.1 × 10−9 mol L−1 to 2.7 × 10−6 mol L−1 (R2 = 0.998); and RSD 4.9% (N = 10 for 1 μmol L−1). These results are compared to screen-printed macroelectrodes (SPEs) giving comparable results providing confidence that AM-electrodes can provide the basis for useful electrochemical sensing platforms. The proposed electroanalytical method (both AM-electrodes and SPEs) is shown to be successfully applied for the determination of manganese(II) in tap water samples and in the analysis of a certified material (drinking water). The proposed method is feasible to be applied for in-loco analyses due to the portability of sensing; in addition, the use of AM-printed electrodes is attractive due to their low cost.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...