A capacitive DNA sensor for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in potable water based on the z3276 genetic marker: fabrication and analytical performance†
Abstract
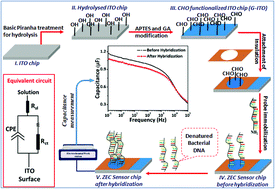
We report a label-free biosensor for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 ATCC 43895 in potable water using a newly designed DNA sensing probe targeting the z3276 genetic marker. The surface of indium tin oxide (ITO) was functionalized with the novel sensing probe by covalent coupling using APTES as a crosslinker to fabricate the DNA sensor (dubbed ZEC [![[z with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_007a_0332.gif) 3276 gene of
3276 gene of ![[E with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0045_0332.gif) .
. ![[c with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0063_0332.gif) oli O157:H7 ATCC 43895]). The electrochemical characterization of the fabricated ZEC sensor was performed using cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Atomic force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy revealed significant changes in the surface topographies of the fabricated ZEC sensor chip. Equivalent circuit analyses suggested the capacitive nature of the ZEC sensor chip, which demonstrated a declining trend of the capacitance value from 1.568 μF (Bare ITO) to 1.221 μF (after DNA hybridization). Non-faradaic sensing measurements revealed systematically declining capacitance values upon DNA hybridization, with a 10 min response time at 10 Hz frequency and 10 mV applied potential. The ZEC sensor chip exhibited linearity in the range of 0.5 to 25 pg per 10 mL for E. coli O157:H7, with ubiquitous cross-validation of each DNA concentration using quantitative PCR prior to the analyses of real water samples. The limit of detection (LOD) at 95% confidence estimated by logistic regression was 0.1 pg DNA per 10 mL of E. coli O157:H7 (equivalent to 13.67 CFU per 10 mL) with a p-value of 0.0237. Consequently, the obtained results demonstrate the possible application of the developed ZEC sensor chip for E. coli O157:H7 detection in real water samples.
oli O157:H7 ATCC 43895]). The electrochemical characterization of the fabricated ZEC sensor was performed using cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Atomic force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy revealed significant changes in the surface topographies of the fabricated ZEC sensor chip. Equivalent circuit analyses suggested the capacitive nature of the ZEC sensor chip, which demonstrated a declining trend of the capacitance value from 1.568 μF (Bare ITO) to 1.221 μF (after DNA hybridization). Non-faradaic sensing measurements revealed systematically declining capacitance values upon DNA hybridization, with a 10 min response time at 10 Hz frequency and 10 mV applied potential. The ZEC sensor chip exhibited linearity in the range of 0.5 to 25 pg per 10 mL for E. coli O157:H7, with ubiquitous cross-validation of each DNA concentration using quantitative PCR prior to the analyses of real water samples. The limit of detection (LOD) at 95% confidence estimated by logistic regression was 0.1 pg DNA per 10 mL of E. coli O157:H7 (equivalent to 13.67 CFU per 10 mL) with a p-value of 0.0237. Consequently, the obtained results demonstrate the possible application of the developed ZEC sensor chip for E. coli O157:H7 detection in real water samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...