A twin enrichment method based on dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and field-amplified sample injection for the simultaneous determination of sulfonamides†
Abstract
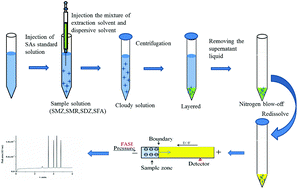
A twin enrichment method based on offline dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) coupled with online field-amplified sample injection (FASI) was developed for the simultaneous determination of four sulfonamide (SA) antibiotics, including sulfamethazine (SMZ), sulfamerazine (SMR), sulfadizine (SDZ) and sulfacetamide (SFA), in different environmental waters, followed by capillary electrophoresis (CE). Various parameters that affected the separation performance of CE and the enrichment efficiencies of DLLME and FASI were optimized in detail, and excellent CE separation was attained within 6 min. The DLLME-FASI-CE offered high sensitivity enrichment factors of 206, 166, 185 and 150 for SMZ, SMR, SDZ and SFA, respectively. Highly sensitive detection was realized with low limits of detection (LODs), which ranged from 2.0–23.0, 2.2–26.0 and 4.3–63.0 ng mL−1 in tap water, lake water and seawater, respectively, as well as limits of quantification (LOQs) within 6.0–63.0, 7.4–96.0 and 14.0–201.0 ng mL−1, respectively. Satisfactory recoveries in the range of 91–108% were obtained with the three spiked environmental water samples, and the relative standard deviations were from 1.09–7.45%. The simple effective twin enrichment method provided promising perspective for CE determination of SAs in complicated aqueous matrices, with rapidity, sensitivity, and accuracy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...