A single-particle enumeration method for the detection of Fe2+ based on a near-infrared core–shell upconversion nanoparticle and IR-808 dye composite nanoprobe†
Abstract
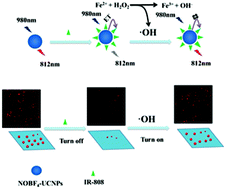
Ferrous ion (Fe2+) is an important component of hemoglobin and plays a role in transporting O2 to human tissues. If iron deficiency is present, iron deficiency anemia may occur, so it is critical to develop sensitive and accurate methods to detect Fe2+. Herein, a novel luminescence energy transfer (ET) system has been designed for the sensitive detection of Fe2+ by a single-particle enumeration (SPE) method in the near-infrared (NIR) region through combining NIR-to-NIR β-NaGdF4:Yb,Tm@NaYF4 upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) and IR-808 dye. IR-808 dye can quench the luminescence of the UCNPs because of the efficient overlap between the absorption spectrum of IR-808 and the emission spectrum of the UCNPs. When Fe2+ and H2O2 are added to the system, the Fenton reaction produces hydroxyl radicals (˙OH). The generated ˙OH reacts with IR-808 and the structure of IR-808 is destroyed. As a result, the ET process is suppressed, causing recovery of the luminescence of the UCNPs, which is reflected as an increase in the number of luminescent particles. Accurate quantification of Fe2+ is achieved by statistically counting the target concentration-dependent luminescent particles. Under the optimal conditions, the linear detection range of Fe2+ is 5–10 000 nM, which is much wider than the ensemble luminescence spectra measurements in bulk solution. Moreover, this strategy can be applied to detection in serum samples with satisfactory results.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...