Addressing the presence of biogenic selenium nanoparticles in yeast cells: analytical strategies based on ICP-TQ-MS†
Abstract
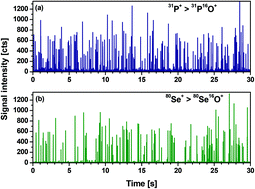
Several organisms have demonstrated the ability of synthesising biogenic selenium-containing nanoparticles. Such particles from biological sources have attracted great attention due to several proven activities as antioxidants or antimicrobial agents. However, little is known in terms of size (distribution), shapes, chemical composition and number/amount/concentration of these particles. Therefore, in this work, we proposed the use of complementary analytical strategies that enabled the detection and characterization of selenium-containing nanoparticles in selenized yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). The first strategy to address the intracellular presence of Se within yeast cells, involves the use of single cell ICP-TQ-MS (inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry). For this aim, selenium and phosphorous (as constitutive element) were measured as oxides (80Se16O+ and 31P16O+, resp.) in the triple-quadrupole mode. Then, a simple and fast cell lysis by mechanical disruption is conducted (approx. 30 min) in order to prove the presence of selenium-containing nanoparticles (SeNPs). The lysate is analysed by single particle ICP-TQ-MS and, complementarily, by liquid chromatography coupled to ICP-TQ-MS to cover a wider range of particle sizes. One of the samples revealed the presence of dispersed SeNPs with sizes between a few nm and up to 250 nm also confirmed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) in the form of elemental selenium. The analysis of the certified reference material SELM-1 showed the presence of spherical SeNPs of 4 to 7 nm diameter. These biogenic particles, at least partially, were made of elemental selenium as well. The whole study reveals the excellent capabilities of “single” event ICP-MS methodologies in combination with HPLC-based strategies for a complete characterization of nanoparticulated material in biological samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...