The determination of trace free acid content in lithium-ion battery electrolytes by coulometric titration in non-aqueous media
Abstract
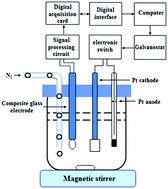
A new quantitative analysis method was proposed, aiming at resolving the difficulty encountered in accurately determining the trace content of a free acid in lithium-ion battery electrolytes in the past 30 years. The presented method overcame the three restrictive factors of lithium-ion battery electrolytes, namely, poor thermal stability, the formation of hydrofluoric acid with water and difficulty in the accurate determination of trace free acids. The free acid in lithium-ion battery electrolytes was directly titrated with ethoxide ions generated through the electrolyzation of a 0.50 mol L−1 LiCl ethanol solution. The content of free acid was obtained according to the Faraday's law, and the whole determination process could be completed in 5 minutes. The relative standard deviation was below 2.0% when the content of free acid was 2.0 μg and above. The detection limit was 1.0 μg and the recovery rate was 99.5%–102.5%. In this method, free acid determination was not affected by temperature change and the existence of a small amount of water. Thus, this study provides a simple, fast and accurate analytical method with a lower detection limit for free acid in the lithium-ion battery industry and comprehensively improves the quality of lithium-ion battery electrolytes and the performance of lithium-ion battery products.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...