Cellulose-based dispersants and flocculants†
Abstract
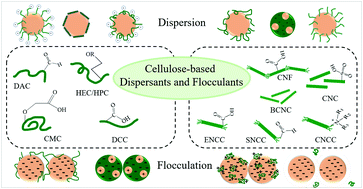
Natural dispersants and flocculants, often referred to as dispersion stabilizers and liquid–solid separators, respectively, have secured a promising role in the bioprocessing community. They have various applications, including in biomedicine and in environmental remediation. A large fraction of existing dispersants and flocculants are synthesized from non-safe chemical compounds such as polyacrylamide and surfactants. Despite numerous advantages of synthetic dispersants and flocculants, issues such as renewability, sustainability, biocompatibility, and cost efficiency have shifted attention towards natural homologues, in particular, cellulose-based ones. Within the past decade, cellulose derivatives, obtained via chemical and mechanical treatments of cellulose fibrils, have successfully been used for these purposes. In this review article, by dividing the functional cellulosic compounds into “polymeric” and “nanoscale” categories, we provide insight into the engineering pathways, the structural frameworks, and surface chemistry of these “green” types of dispersants and flocculants. A summary of their efficiency and the controlling parameters is also accompanied by recent advances in their applications in each section. We are confident that the emergence of cellulose-based dispersing and flocculating agents will extend the boundaries of sustainable green technology.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry B Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...