Polymer microneedles with interconnected porous structures via a phase inversion route for transdermal medical applications†
Abstract
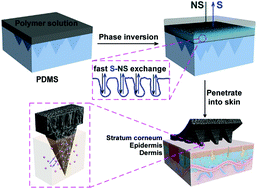
Porous polymer microneedles (MNs) have great potential in transdermal medical applications due to their three-dimensional (3D) porous structures and high porosity. However, existing approaches for the fabrication of such porous polymer MNs are complicated and only applicable to limited types of polymers. Here, we describe a facile yet effective phase inversion route to prepare polymer MNs with highly porous and interconnected pore structures. The fabrication process is simple and mild without involving high temperatures or irradiation, and can be applied to a broad spectrum of commonly used polymers (e.g., cellulose acetate (CA), polysulfone (PSF), polyethersulfone (PES), polylactic acid (PLA), etc.). Thanks to the capillary effect and large cavity given by highly porous and interconnected structures, the resulting porous polymer MNs show the capability of rapidly extracting dermal interstitial fluid (ISF) and efficiently loading/releasing drug compounds. As a proof of concept, we demonstrate the use of these porous CA MNs in the highly efficient extraction of ISF for glucose level detection and administration of insulin for hyperglycemia. Given the recent trend of painless techniques in diagnosis and treatment, the current study provides a new opportunity for the fabrication of MN-based devices for transdermal ISF extraction and drug delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...